Measuring Software Size Exercises
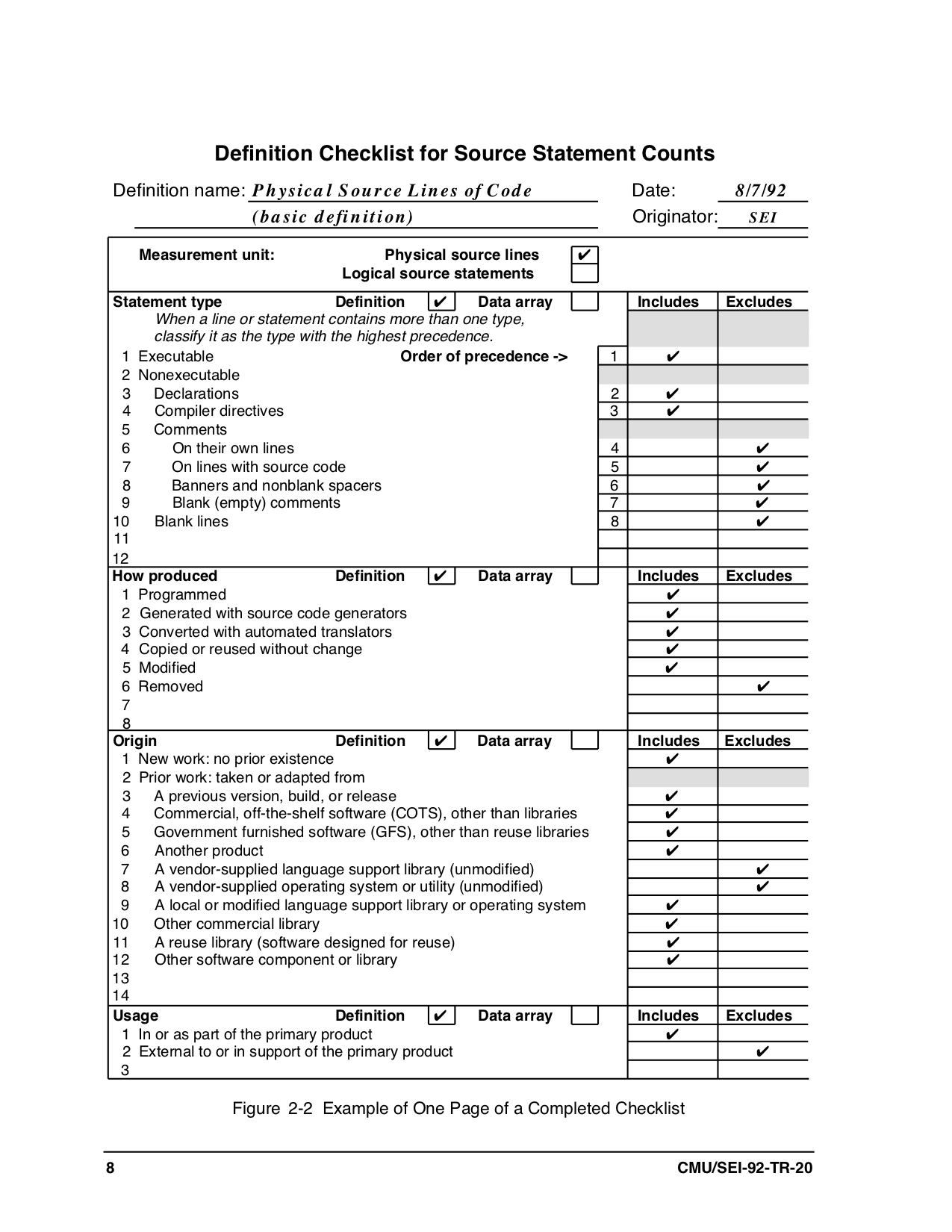
- Software Engineering Institute's code counting checklist (originally published here):
- Discuss the following quote with your neighbor. Do you agree or disagree with it? Why?:
"A proficient programmer can program approximately the same number of debugged lines of code per day regardless of the language"
(From Software Measurement and Estimation by Linda M. Laird and M. Carol Brennan) - Look at a gearing factors table (e.g., QSM's Function Point Languages Table). What does this mean? What language would you choose?
- Your boss wants to know how long a project will take. The requirements document has 200 requirements. Empirically, your group requires about 1.25 staff months per requirement (with a standard deviation of 9%).
- What questions should you answer?
- What do you tell your boss?
- Functional Points
Given the function point complexity ratings below:
For a small program with 5 simple inputs, 2 basic data files and 3 outputs, what is the unadjusted function points?Component Simple Average Complex Inputs 3 4 6 Outputs 4 5 7 Data Files 7 10 15 Interfaces 5 7 10 Inquires 3 4 6 - General System Characteristic Brief Descriptions:
- Data communications How many communication facilities are there to aid in the transfer or exchange of information with the application or system?
- Distributed data processing How are distributed data and processing functions handled?
- Performance Did the user require response time or throughput?
- Heavily used configuration How heavily used is the current hardware platform where the application will be executed?
- Transaction rate How frequently are transactions executed daily, weekly, monthly, etc.?
- On-Line data entry What percentage of the information is entered On-Line?
- End-user efficiency Was the application designed for end-user efficiency?
- On-Line update How many ILF’s are updated by On-Line transaction?
- Complex processing Does the application have extensive logical or mathematical processing?
- Reusability Was the application developed to meet one or many user’s needs?
- Installation ease How difficult is conversion and installation?
- Operational ease How effective and/or automated are start-up, back up, and recovery procedures?
- Multiple sites Was the application specifically designed, developed, and supported to be installed at multiple sites for multiple organizations?
- Facilitate change Was the application specifically designed, developed, and supported to facilitate change?