LAB 7 - Introduction to Programming (part 2 - turtles)
Lab Exercises
Topics
n To introduce computation as simulation
n To introduce the turtle and talk about the history of using turtles to teach programming
n To show how to add classes to the classpath in DrJava
n To create objects in Java
Exercises
3.4 Working with Turtles
3.4.1 Defining Classes
Make sure the classpath is set to include the classes from the book:
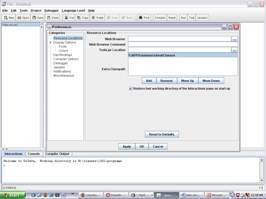
3.4.2 Creating Objects
Create a world named myWorld:
> World myWorld;
> myWorld = new World();
>System.out.println(myWorld); //calls toString method for the myWorld object
[Find World in the API for the Book Classes]
Create a turtle named myTurtle on myWorld
>Turtle myTurtle;
> myTurtle = new Turtle (myWorld);
> System.out.println(myTurtle);
[Find Turtle (and SimpleTurtle) in the API for the Book Classes]
Create a second turtle named yourTurtle on myWorld at x=40, y=50
>Turtle yourTurtle;
> yourTurtle = new Turtle (40, 50, myWorld);
> System.out.println(yourTurtle);
3.4.3 Sending Messages to Objects
Use forward(), forward(x), backward, backward(x), turnLeft(), turnRight(), and turn(x) to move the two turtles around the world where x can be positive or negative integers
3.4.4 Objects Control Their State
Try making one of the turtles to leave the world (use a large value for x)
Where is the turtle (“print” the turtle to find out)
3.4.5 Additional Turtle Capabilities
Explore other SimpleTurtle methods (hide, show, penUp, penDown, moveTo) to draw squares, the letter T, and other objects
QUESTIONS:
Submit the answers through the DropBox in WebCT.